Qwen3-Max-Thinking state-of-the-art reasoning model at your fingertips!

Qwen/
Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Instruct
$0.09
in
$1.10
out
/ 1M tokens
Over the past few months, we have observed increasingly clear trends toward scaling both total parameters and context lengths in the pursuit of more powerful and agentic artificial intelligence (AI). We are excited to share our latest advancements in addressing these demands, centered on improving scaling efficiency through innovative model architecture. We call this next-generation foundation models Qwen3-Next.


Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Instruct
Ask me anything
Settings
library_name: transformers license: apache-2.0 license_link: https://huggingface.co/Qwen/Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Instruct/blob/main/LICENSE pipeline_tag: text-generation
Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Instruct

Over the past few months, we have observed increasingly clear trends toward scaling both total parameters and context lengths in the pursuit of more powerful and agentic artificial intelligence (AI). We are excited to share our latest advancements in addressing these demands, centered on improving scaling efficiency through innovative model architecture. We call this next-generation foundation models Qwen3-Next.
Highlights
Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B is the first installment in the Qwen3-Next series and features the following key enchancements:
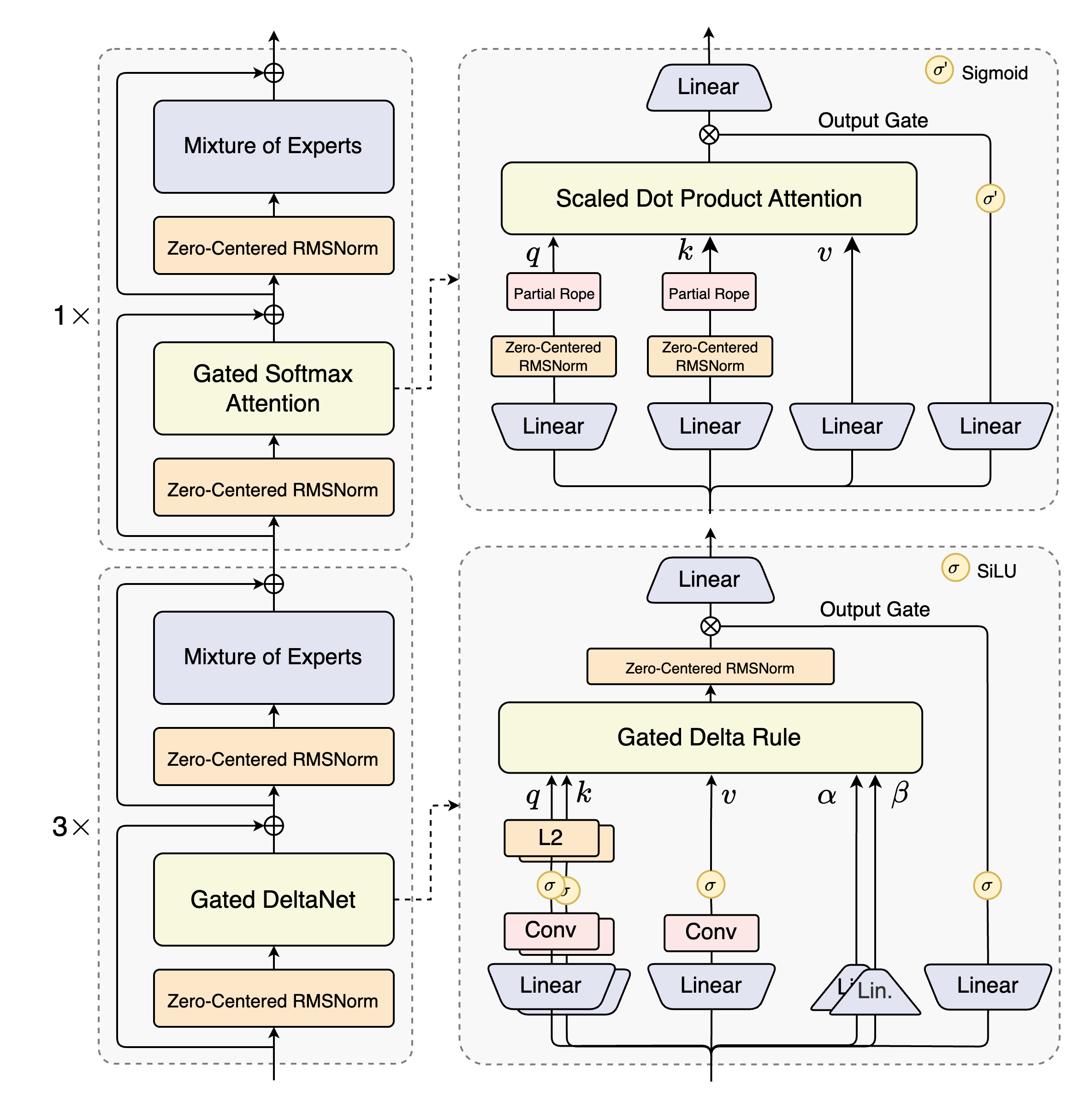
- Hybrid Attention: Replaces standard attention with the combination of Gated DeltaNet and Gated Attention, enabling efficient context modeling for ultra-long context length.
- High-Sparsity Mixture-of-Experts (MoE): Achieves an extreme low activation ratio in MoE layers, drastically reducing FLOPs per token while preserving model capacity.
- Stability Optimizations: Includes techniques such as zero-centered and weight-decayed layernorm, and other stabilizing enhancements for robust pre-training and post-training.
- Multi-Token Prediction (MTP): Boosts pretraining model performance and accelerates inference.
We are seeing strong performance in terms of both parameter efficiency and inference speed for Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B:
- Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Base outperforms Qwen3-32B-Base on downstream tasks with 10% of the total training cost and with 10 times inference throughput for context over 32K tokens.
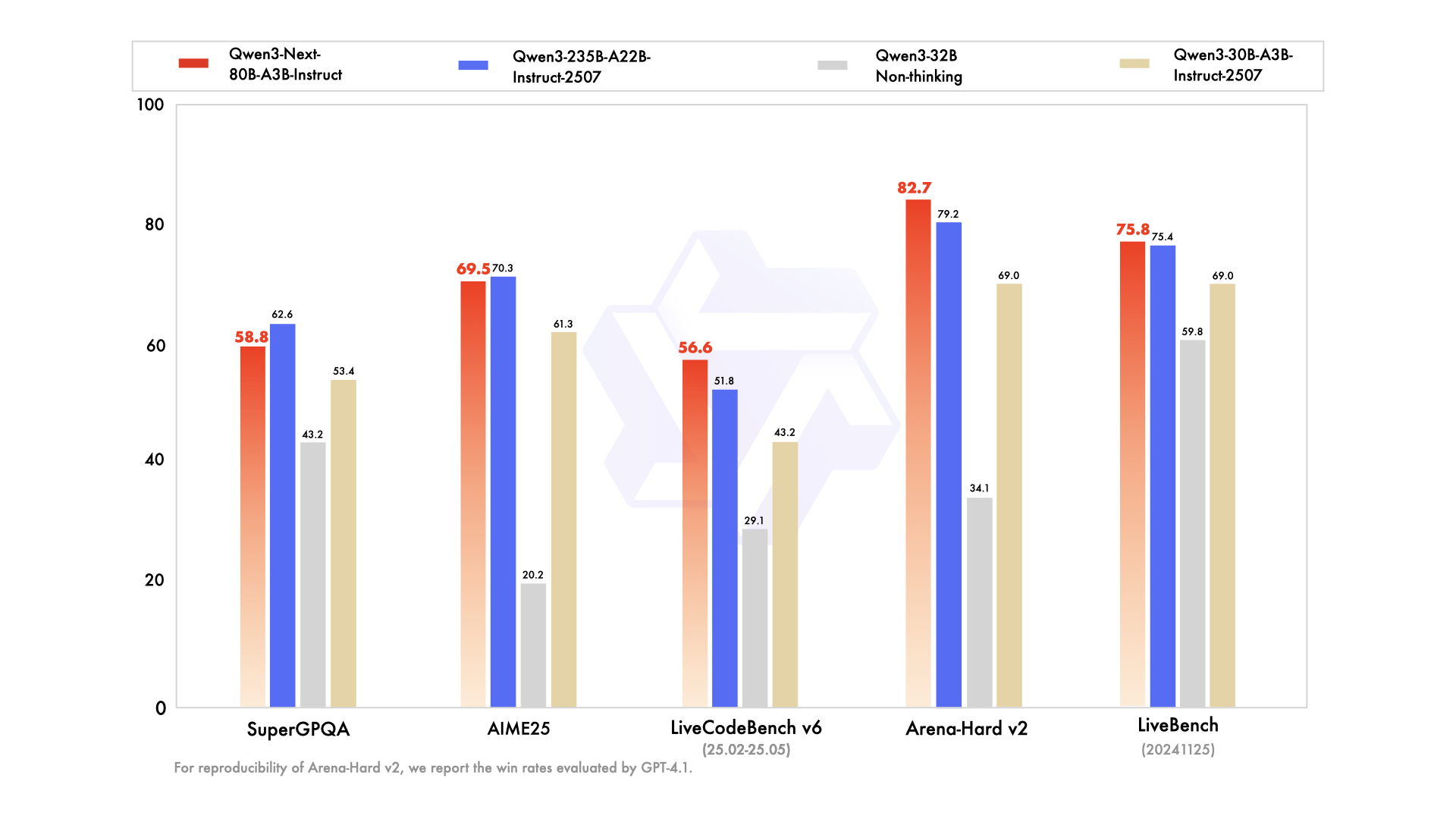
- Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Instruct performs on par with Qwen3-235B-A22B-Instruct-2507 on certain benchmarks, while demonstrating significant advantages in handling ultra-long-context tasks up to 256K tokens.
For more details, please refer to our blog post Qwen3-Next.
Model Overview
[!Note] Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Instruct supports only instruct (non-thinking) mode and does not generate
**\<think>****\</think>**blocks in its output.
Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Instruct has the following features:
- Type: Causal Language Models
- Training Stage: Pretraining (15T tokens) & Post-training
- Number of Parameters: 80B in total and 3B activated
- Number of Paramaters (Non-Embedding): 79B
- Number of Layers: 48
- Hidden Dimension: 2048
- Hybrid Layout: 12 * (3 * (Gated DeltaNet -> MoE) -> (Gated Attention -> MoE))
- Gated Attention:
- Number of Attention Heads: 16 for Q and 2 for KV
- Head Dimension: 256
- Rotary Position Embedding Dimension: 64
- Gated DeltaNet:
- Number of Linear Attention Heads: 32 for V and 16 for QK
- Head Dimension: 128
- Mixture of Experts:
- Number of Experts: 512
- Number of Activated Experts: 10
- Number of Shared Experts: 1
- Expert Intermediate Dimension: 512
- Context Length: 262,144 natively and extensible up to 1,010,000 tokens
Performance
| Qwen3-30B-A3B-Instruct-2507 | Qwen3-32B Non-Thinking | Qwen3-235B-A22B-Instruct-2507 | Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Instruct | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Knowledge | ||||
| MMLU-Pro | 78.4 | 71.9 | 83.0 | 80.6 |
| MMLU-Redux | 89.3 | 85.7 | 93.1 | 90.9 |
| GPQA | 70.4 | 54.6 | 77.5 | 72.9 |
| SuperGPQA | 53.4 | 43.2 | 62.6 | 58.8 |
| Reasoning | ||||
| AIME25 | 61.3 | 20.2 | 70.3 | 69.5 |
| HMMT25 | 43.0 | 9.8 | 55.4 | 54.1 |
| LiveBench 20241125 | 69.0 | 59.8 | 75.4 | 75.8 |
| Coding | ||||
| LiveCodeBench v6 (25.02-25.05) | 43.2 | 29.1 | 51.8 | 56.6 |
| MultiPL-E | 83.8 | 76.9 | 87.9 | 87.8 |
| Aider-Polyglot | 35.6 | 40.0 | 57.3 | 49.8 |
| Alignment | ||||
| IFEval | 84.7 | 83.2 | 88.7 | 87.6 |
| Arena-Hard v2* | 69.0 | 34.1 | 79.2 | 82.7 |
| Creative Writing v3 | 86.0 | 78.3 | 87.5 | 85.3 |
| WritingBench | 85.5 | 75.4 | 85.2 | 87.3 |
| Agent | ||||
| BFCL-v3 | 65.1 | 63.0 | 70.9 | 70.3 |
| TAU1-Retail | 59.1 | 40.1 | 71.3 | 60.9 |
| TAU1-Airline | 40.0 | 17.0 | 44.0 | 44.0 |
| TAU2-Retail | 57.0 | 48.8 | 74.6 | 57.3 |
| TAU2-Airline | 38.0 | 24.0 | 50.0 | 45.5 |
| TAU2-Telecom | 12.3 | 24.6 | 32.5 | 13.2 |
| Multilingualism | ||||
| MultiIF | 67.9 | 70.7 | 77.5 | 75.8 |
| MMLU-ProX | 72.0 | 69.3 | 79.4 | 76.7 |
| INCLUDE | 71.9 | 70.9 | 79.5 | 78.9 |
| PolyMATH | 43.1 | 22.5 | 50.2 | 45.9 |
*: For reproducibility, we report the win rates evaluated by GPT-4.1.
Quickstart
The code for Qwen3-Next has been merged into the main branch of Hugging Face transformers.
pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@main
With earlier versions, you will encounter the following error:
KeyError: 'qwen3_next'
The following contains a code snippet illustrating how to use the model generate content based on given inputs.
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
model_name = "Qwen/Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Instruct"
# load the tokenizer and the model
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_name,
dtype="auto",
device_map="auto",
)
# prepare the model input
prompt = "Give me a short introduction to large language model."
messages = [
{"role": "user", "content": prompt},
]
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=False,
add_generation_prompt=True,
)
model_inputs = tokenizer([text], return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
# conduct text completion
generated_ids = model.generate(
**model_inputs,
max_new_tokens=16384,
)
output_ids = generated_ids[0][len(model_inputs.input_ids[0]):].tolist()
content = tokenizer.decode(output_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
print("content:", content)
[!Note] Multi-Token Prediction (MTP) is not generally available in Hugging Face Transformers.
[!Note] The efficiency or throughput improvement depends highly on the implementation. It is recommended to adopt a dedicated inference framework, e.g., SGLang and vLLM, for inference tasks.
[!Tip] Depending on the inference settings, you may observe better efficiency with
flash-linear-attentionandcausal-conv1d. See the above links for detailed instructions and requirements.
Deployment
For deployment, you can use the latest sglang or vllm to create an OpenAI-compatible API endpoint.
SGLang
SGLang is a fast serving framework for large language models and vision language models. SGLang could be used to launch a server with OpenAI-compatible API service.
SGLang has supported Qwen3-Next in its main branch, which can be installed from source:
pip install 'sglang[all] @ git+https://github.com/sgl-project/sglang.git@main#subdirectory=python'
The following command can be used to create an API endpoint at http://localhost:30000/v1 with maximum context length 256K tokens using tensor parallel on 4 GPUs.
SGLANG_ALLOW_OVERWRITE_LONGER_CONTEXT_LEN=1 python -m sglang.launch_server --model-path Qwen/Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Instruct --port 30000 --tp-size 4 --context-length 262144 --mem-fraction-static 0.8
The following command is recommended for MTP with the rest settings the same as above:
SGLANG_ALLOW_OVERWRITE_LONGER_CONTEXT_LEN=1 python -m sglang.launch_server --model-path Qwen/Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Instruct --port 30000 --tp-size 4 --context-length 262144 --mem-fraction-static 0.8 --speculative-algo NEXTN --speculative-num-steps 3 --speculative-eagle-topk 1 --speculative-num-draft-tokens 4
[!Note] The environment variable
SGLANG_ALLOW_OVERWRITE_LONGER_CONTEXT_LEN=1is required at the moment.
[!Note] The default context length is 256K. Consider reducing the context length to a smaller value, e.g.,
32768, if the server fail to start.
vLLM
vLLM is a high-throughput and memory-efficient inference and serving engine for LLMs. vLLM could be used to launch a server with OpenAI-compatible API service.
vLLM has supported Qwen3-Next in its main branch, which can be installed from source:
pip install git+https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm.git
The following command can be used to create an API endpoint at http://localhost:8000/v1 with maximum context length 256K tokens using tensor parallel on 4 GPUs.
VLLM_ALLOW_LONG_MAX_MODEL_LEN=1 vllm serve Qwen/Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Instruct --port 8000 --tensor-parallel-size 4 --max-model-len 262144
The following command is recommended for MTP with the rest settings the same as above:
VLLM_ALLOW_LONG_MAX_MODEL_LEN=1 vllm serve Qwen/Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Instruct --port 8000 --tensor-parallel-size 4 --max-model-len 262144 --speculative-config '{"method":"qwen3_next_mtp","num_speculative_tokens":2}'
[!Note] The environment variable
VLLM_ALLOW_LONG_MAX_MODEL_LEN=1is required at the moment.
[!Note] The default context length is 256K. Consider reducing the context length to a smaller value, e.g.,
32768, if the server fail to start.
Agentic Use
Qwen3 excels in tool calling capabilities. We recommend using Qwen-Agent to make the best use of agentic ability of Qwen3. Qwen-Agent encapsulates tool-calling templates and tool-calling parsers internally, greatly reducing coding complexity.
To define the available tools, you can use the MCP configuration file, use the integrated tool of Qwen-Agent, or integrate other tools by yourself.
from qwen_agent.agents import Assistant
# Define LLM
llm_cfg = {
'model': 'Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Instruct',
# Use a custom endpoint compatible with OpenAI API:
'model_server': 'http://localhost:8000/v1', # api_base
'api_key': 'EMPTY',
}
# Define Tools
tools = [
{'mcpServers': { # You can specify the MCP configuration file
'time': {
'command': 'uvx',
'args': ['mcp-server-time', '--local-timezone=Asia/Shanghai']
},
"fetch": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": ["mcp-server-fetch"]
}
}
},
'code_interpreter', # Built-in tools
]
# Define Agent
bot = Assistant(llm=llm_cfg, function_list=tools)
# Streaming generation
messages = [{'role': 'user', 'content': 'https://qwenlm.github.io/blog/ Introduce the latest developments of Qwen'}]
for responses in bot.run(messages=messages):
pass
print(responses)
Processing Ultra-Long Texts
Qwen3-Next natively supports context lengths of up to 262,144 tokens. For conversations where the total length (including both input and output) significantly exceeds this limit, we recommend using RoPE scaling techniques to handle long texts effectively. We have validated the model's performance on context lengths of up to 1 million tokens using the YaRN method.
YaRN is currently supported by several inference frameworks, e.g., transformers, vllm and sglang.
In general, there are two approaches to enabling YaRN for supported frameworks:
-
Modifying the model files: In the
config.jsonfile, add therope_scalingfields:{ ..., "rope_scaling": { "rope_type": "yarn", "factor": 4.0, "original_max_position_embeddings": 262144 } } -
Passing command line arguments:
For
vllm, you can useVLLM_ALLOW_LONG_MAX_MODEL_LEN=1 vllm serve ... --rope-scaling '{"rope_type":"yarn","factor":4.0,"original_max_position_embeddings":262144}' --max-model-len 1010000For
sglang, you can useSGLANG_ALLOW_OVERWRITE_LONGER_CONTEXT_LEN=1 python -m sglang.launch_server ... --json-model-override-args '{"rope_scaling":{"rope_type":"yarn","factor":4.0,"original_max_position_embeddings":262144}}' --context-length 1010000
[!NOTE] All the notable open-source frameworks implement static YaRN, which means the scaling factor remains constant regardless of input length, potentially impacting performance on shorter texts. We advise adding the
rope_scalingconfiguration only when processing long contexts is required. It is also recommended to modify thefactoras needed. For example, if the typical context length for your application is 524,288 tokens, it would be better to setfactoras 2.0.
Long-Context Performance
We test the model on an 1M version of the RULER benchmark.
| Model Name | Acc avg | 4k | 8k | 16k | 32k | 64k | 96k | 128k | 192k | 256k | 384k | 512k | 640k | 768k | 896k | 1000k |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qwen3-30B-A3B-Instruct-2507 | 86.8 | 98.0 | 96.7 | 96.9 | 97.2 | 93.4 | 91.0 | 89.1 | 89.8 | 82.5 | 83.6 | 78.4 | 79.7 | 77.6 | 75.7 | 72.8 |
| Qwen3-235B-A22B-Instruct-2507 | 92.5 | 98.5 | 97.6 | 96.9 | 97.3 | 95.8 | 94.9 | 93.9 | 94.5 | 91.0 | 92.2 | 90.9 | 87.8 | 84.8 | 86.5 | 84.5 |
| Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Instruct | 91.8 | 98.5 | 99.0 | 98.0 | 98.7 | 97.6 | 95.0 | 96.0 | 94.0 | 93.5 | 91.7 | 86.9 | 85.5 | 81.7 | 80.3 | 80.3 |
- Qwen3-Next are evaluated with YaRN enabled. Qwen3-2507 models are evaluated with Dual Chunk Attention enabled.
- Since the evaluation is time-consuming, we use 260 samples for each length (13 sub-tasks, 20 samples for each).
Best Practices
To achieve optimal performance, we recommend the following settings:
-
Sampling Parameters:
- We suggest using
Temperature=0.7,TopP=0.8,TopK=20, andMinP=0. - For supported frameworks, you can adjust the
presence_penaltyparameter between 0 and 2 to reduce endless repetitions. However, using a higher value may occasionally result in language mixing and a slight decrease in model performance.
- We suggest using
-
Adequate Output Length: We recommend using an output length of 16,384 tokens for most queries, which is adequate for instruct models.
-
Standardize Output Format: We recommend using prompts to standardize model outputs when benchmarking.
- Math Problems: Include "Please reason step by step, and put your final answer within \boxed{}." in the prompt.
- Multiple-Choice Questions: Add the following JSON structure to the prompt to standardize responses: "Please show your choice in the
answerfield with only the choice letter, e.g.,"answer": "C"."
Citation
If you find our work helpful, feel free to give us a cite.
@misc{qwen3technicalreport,
title={Qwen3 Technical Report},
author={Qwen Team},
year={2025},
eprint={2505.09388},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.09388},
}
@article{qwen2.5-1m,
title={Qwen2.5-1M Technical Report},
author={An Yang and Bowen Yu and Chengyuan Li and Dayiheng Liu and Fei Huang and Haoyan Huang and Jiandong Jiang and Jianhong Tu and Jianwei Zhang and Jingren Zhou and Junyang Lin and Kai Dang and Kexin Yang and Le Yu and Mei Li and Minmin Sun and Qin Zhu and Rui Men and Tao He and Weijia Xu and Wenbiao Yin and Wenyuan Yu and Xiafei Qiu and Xingzhang Ren and Xinlong Yang and Yong Li and Zhiying Xu and Zipeng Zhang},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2501.15383},
year={2025}
}

© 2026 Deep Infra. All rights reserved.

